
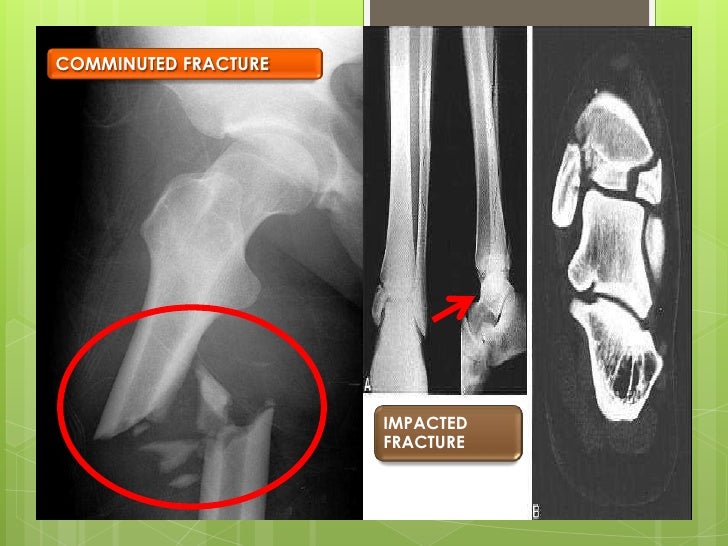
In contrast, depressed fractures will often require surgical intervention for cosmesis and reduction in the incidence of post-traumatic epilepsy 1. Skull fractures, if closed and undisplaced, rarely need any direct management, with treatment being aimed at any associated injury (e.g. MRI is insensitive to fractures and it is often frightening how difficult it is to visualize fractures even when they are prominent and already known about on CT. Underlying cerebral hemorrhagic contusionsĭural tears leading to CSF leak and intracranial hypotension direct caroticocavernous fistula)Įxtension through cranial nerve foramina or canals with neural damage Examples of soft tissue injuries include:Īrterial dissection, occlusion or ruptureĪrteriovenous fistula (e.g. Separation of the growth plate from the bone is. Common proximal tibial fractures include: Proximal Tibial Epiphyseal Fracture: This type of fracture affects the top portion of the bone (epiphysis) and the growth plate. When a fracture is identified, a careful search for adjacent soft tissue injury should be undertaken. Depending on the exact location, a proximal tibial fracture may affect the stability of the knee as well as the growth plate. Almost invariably, if the fracture involves a paranasal sinus, middle ear or mastoid air cells, then they will contain some blood, which is a helpful clue to the presence of an underlying fracture. They need to be distinguished from normal sutures, which have corticated margins that fractures lack. It is essential that a bone algorithm is used if undisplaced fractures are to be visualized.įractures will appear as discontinuities in the bone and may or may not be displaced. Furthermore, it is obtained at the same time as the brain is imaged.ĬT of the skull should be obtained volumetrically with small (<1 mm) voxels and be able to be reconstructed in multiple planes. Not only is CT sensitive to the detection fractures but it is also able to exquisitely characterize their extent and allow for surgical planning. Skull fractures are best imaged with CT of the brain. They are no longer recommended to assess head injuries unless as part of a skeletal survey for a suspected non-accidental injury of a child 5. Plain radiographs have a limited role and are superseded by CT scans.

The pattern of fracturing depends on the location, direction and kinetic properties of the impact as well as intrinsic features of the skull 2-4. Skull fractures can be broadly divided in a variety of ways:įractures of the skull, as with fractures of any bone, occur when biomechanical stresses exceed the bone's tolerance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
